What is Water Recycling Systems and How Do They Work in Everyday Life
Water recycling systems have emerged as a vital technology in addressing global water scarcity, making significant contributions in both urban and agricultural settings. According to a report by the United Nations, by 2025, nearly 1.8 billion people will be living in areas plagued by water scarcity, emphasizing the urgent need for sustainable water management solutions. These systems efficiently treat and reuse wastewater, reducing the demand for freshwater resources while also minimizing environmental impact.
Dr. Jane Smith, a renowned expert in water resource management, emphasizes the importance of these systems, stating, "Water recycling systems not only provide an alternative source of water but also play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and resilience in communities." As urban populations continue to grow, innovative and effective water recycling systems are being implemented to ensure that cities can thrive without depleting their water resources.
Moreover, the economic benefits of water recycling systems are equally compelling. A recent study by the Water Environment Federation indicated that investing in water recycling and reuse technologies could save municipalities millions of dollars in water supply costs. Thus, understanding and adopting water recycling systems is essential for a sustainable future, where both human needs and environmental conservation can coexist harmoniously.

What is Water Recycling?
Water recycling, also known as water reclamation or reuse, is the process of collecting, treating, and repurposing wastewater for various applications. This essential practice not only conserves water but also helps reduce pollution and the demand on natural water sources. According to the United Nations, the world is expected to face a significant freshwater shortage, with an estimated 5 billion people potentially living in water-scarce regions by 2050. Water recycling systems offer a sustainable solution that can be implemented in both residential and commercial settings.
In everyday life, water recycling systems function through several stages. Initially, wastewater is collected from sinks, showers, and toilets, typically through a network of pipes. This water then undergoes treatment processes, which may include filtration, chemical treatments, and biological processes to remove contaminants. Once treated, the reclaimed water can be used for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation, toilet flushing, and even in industrial applications. Research from the Water Environment Federation indicates that cities can reclaim up to 50% of their wastewater, significantly enhancing water availability.
Tips for integrating water recycling into daily life include installing greywater systems, which allow for the reuse of water from baths and sinks to irrigate gardens. Additionally, consider utilizing rainwater harvesting solutions to supplement your water supply. By adopting these methods, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable water future while reducing their overall water consumption.
Water Recycling Systems: Usage in Everyday Life
The above chart represents the amount of water recycled across different sectors in a month. Residential areas recycle approximately 20 million gallons, while municipal systems lead with 40 million gallons, showcasing the significant impact of water recycling initiatives in various sectors of daily life.
Importance of Water Recycling in Everyday Life
Water recycling, also known as water reclamation, plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability and addressing the growing concerns of water scarcity faced by many communities. By treating and reusing wastewater, water recycling systems can significantly reduce the demand for fresh water sources. This process not only conserves precious resources but also minimizes the environmental impact of wastewater disposal, making it a vital practice in urban planning and water management.
In everyday life, water recycling contributes to a circular economy where water is constantly repurposed and reused. For instance, greywater systems can collect water from sinks, showers, and laundry, filtering it for reuse in irrigation or toilet flushing. This practice not only lowers water bills for households but also decreases the pressure on municipal water supplies.
Additionally, many industries utilize water recycling systems to treat and reuse their process water, reducing operational costs and enhancing water efficiency. Overall, the importance of water recycling lies in its ability to foster resilience against water shortages while promoting responsible water use in our daily routines.
How Water Recycling Systems Function
 Water recycling systems are designed to collect, treat, and reuse water from various sources to ensure sustainable water use. These systems typically include several processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and disinfection, allowing them to efficiently convert wastewater into clean water suitable for a variety of applications. In everyday life, water recycling plays a crucial role in conserving resources, especially in areas facing water scarcity.
Water recycling systems are designed to collect, treat, and reuse water from various sources to ensure sustainable water use. These systems typically include several processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and disinfection, allowing them to efficiently convert wastewater into clean water suitable for a variety of applications. In everyday life, water recycling plays a crucial role in conserving resources, especially in areas facing water scarcity.
The functionality of a water recycling system begins with the collection of greywater from domestic sources, such as sinks, showers, and washing machines. Once collected, this water undergoes an initial screening to remove large debris. Following this, it is subjected to various treatment stages, including biological processes that utilize microorganisms to break down organic matter. Advanced filtration techniques, such as membrane filtration, further purify the water, and finally, disinfection methods like UV treatment or chlorination ensure that harmful pathogens are eliminated. The treated water can then be used for non-potable purposes such as irrigation, toilet flushing, or even cooling systems, significantly reducing demand on freshwater resources.
Types of Water Recycling Systems
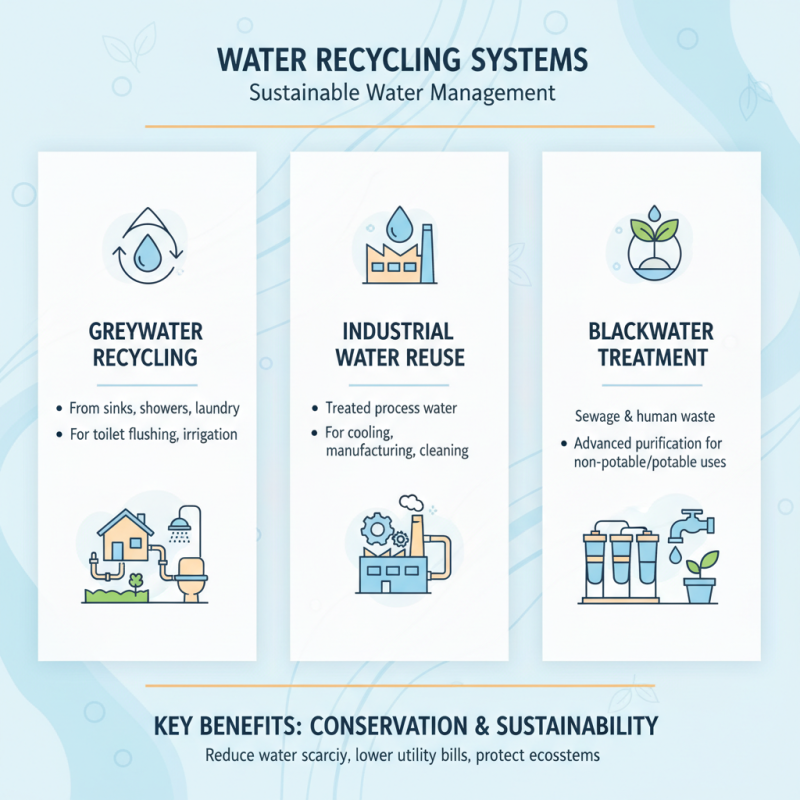
Water recycling systems play a crucial role in conserving resources and ensuring sustainable water management in our daily lives. There are several types of water recycling systems that are widely used, each serving unique purposes and applications.
One common type is the greywater recycling system, which collects water from sinks, showers, and washing machines. This water, which is relatively clean but not suitable for drinking, can be treated and reused for irrigation, toilet flushing, and even cooling systems. By utilizing greywater, households can significantly reduce their freshwater consumption and promote water sustainability.
Another prevalent system is the rainwater harvesting system, which captures and stores rainwater for later use. This system often consists of gutters, storage tanks, and filtration devices that ensure the collected water is safe for various applications. Rainwater can be used for irrigation, cleaning, and even drinking water, depending on the level of treatment it undergoes. By implementing rainwater harvesting, communities can enhance their resilience to water scarcity and minimize the reliance on traditional water sources.
Applications of Recycled Water in Various Sectors
Recycled water plays a crucial role in various sectors, providing an innovative solution to water scarcity while promoting sustainability. In agriculture, treated wastewater is often repurposed for irrigation, significantly reducing the demand for freshwater sources. This practice not only helps conserve water but also improves crop yields, making farming more resilient to climate variations. Additionally, many farms have adopted advanced purification techniques, ensuring that recycled water meets the necessary safety standards for use in food production.
In urban settings, recycled water is used for non-potable applications such as landscape irrigation, street cleaning, and toilet flushing in commercial buildings. By diverting wastewater for these purposes, cities can alleviate pressure on their water supply systems, especially during drought conditions. Furthermore, industries are increasingly utilizing recycled water in manufacturing processes, cooling systems, and even in the production of energy, demonstrating the versatility of reclaimed water. These applications not only help conserve vital resources but also contribute to the economic efficiency of various sectors by reducing reliance on conventional water supplies.
What is Water Recycling Systems and How Do They Work in Everyday Life - Applications of Recycled Water in Various Sectors
| Sector | Application | Type of Recycled Water | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Irrigation | Treated wastewater | Conserves freshwater, reduces costs |
| Industry | Cooling water | Process water | Reduces water demand, lowers waste discharge |
| Residential | Landscape irrigation | Greywater | Decreases water utility bills, promotes sustainable living |
| Recreation | Watering golf courses | Reclaimed water | Enhances aesthetics, lowers maintenance costs |
| Construction | Dust control and mixing | Recycled water | Saves potable water, reduces project costs |
Related Posts
-

Revolutionizing Sustainability: Top Water Recycling Systems to Watch in 2025
-

Innovative Water System Solutions for Sustainable Urban Development
-

Exploring the Essential Role of Water Systems in Sustainable Urban Development and Climate Resilience
-

How to Choose the Best System Water for Your Home and Health Needs
-

Why Understanding Water Systems is Essential for Sustainable Living
-

How to Choose the Best Water Conditioning Systems for Your Home
